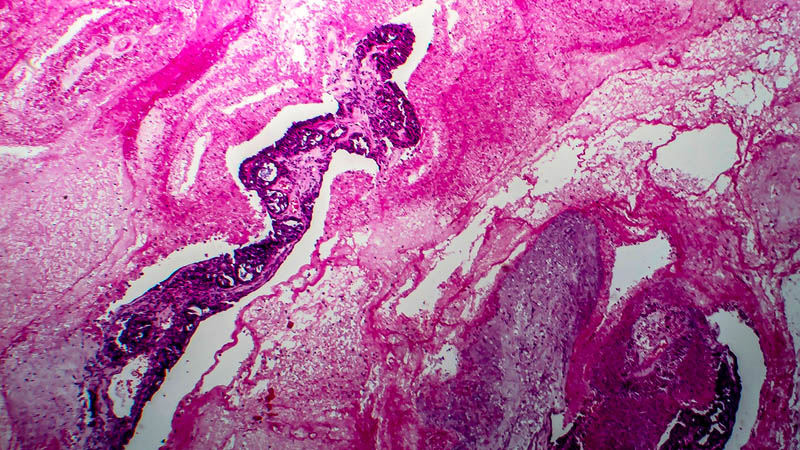
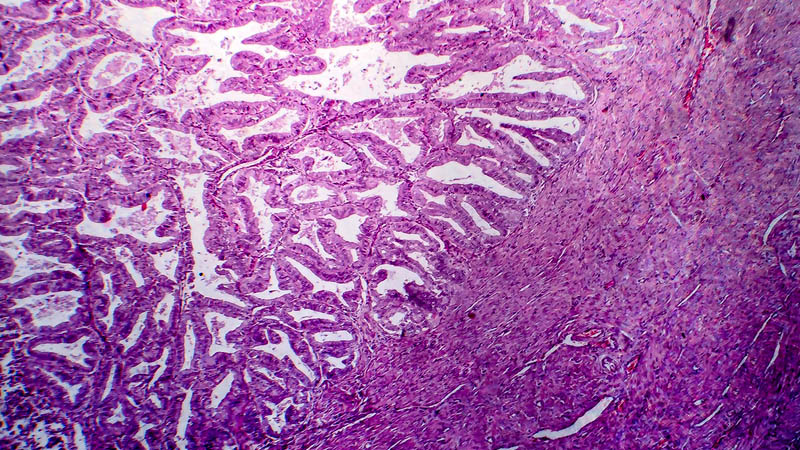
Selected molecular factors associated with metastases of ovarian cancer
Anna Markowska1, Jolanta Lubin2, Karolina Jaszczyńska-Nowinka2, Janina Markowska2
 Affiliacja i adres do korespondencji
Affiliacja i adres do korespondencjiDevelopment of metastases is a typical feature of cancer progression and the main cause of treatment failure in cancer treatment. Due to their ability to settle far from original tumor location, cancer cells may preserve the feature of immortal cells, enabling survival of tumor and transition to chronic phase of the disease. Applying currently available techniques of topical treatment, such as surgery and radiotherapy, we are unable to control fully spread of cancer cells, while systemic chemotherapy even in chemosensitive tumors does not eradicate the disease in all cases. Ovarian cancer may spread by dissemination within the abdominal cavity and lymphatic vessels, resulting in distant metastases. The process of metastases’ development is extremely complex, depending on many different factors governing intercellular adhesion and acquisition of ability to move and migrate by cancer cells. Tumors with coexisting distant metastases are considered most advanced, which means also a grim prognosis for the patient. Mechanism of metastases’ development is the subject of several studies, attempting to identify factors which might lend themselves for targeted therapy of cancers, including ovarian cancer. The paper presents genes, their products and other metastases-associated proteins: HER2 gene, AEG-1 gene, kisspeptin, E-cadherin, survivin, uPAR, clusterin, Met gene, claudins 3 and 4, kallikreins, SDF-1 gene. This paper is meant to systematize extensive knowledge on the development of metastases development and synthetic analysis of data concerning this process.